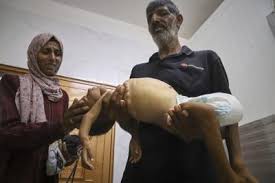
KHAN YOUNIS, Gaza Strip— The dead body of 2 1/2-year-old Ro’a Mashi lay on the table in Gaza’s Nasser Hospital, her arms and rib cage skeletal, her eyes sunken in her skull. Doctors say she had no preexisting conditions and wasted away over months as her family struggled to find food and treatment.
Her family showed The Associated Press a photo of Ro’a’s body at the hospital, and it was confirmed by the doctor who received her remains. Several days after she died, Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu on Sunday told local media, “There is no hunger. There was no hunger. There was a shortage, and there was certainly no policy of starvation.”
In the face of international outcry, Netanyahu has pushed back, saying reports of starvation are “lies” promoted by Hamas.
However, U.N. spokesman Stephane Dujarric this week warned that starvation and malnutrition in Gaza are at the highest levels since the war began.
The U.N. says nearly 12,000 children under 5 were found to have acute malnutrition in July — including more than 2,500 with severe malnutrition, the most dangerous level. The World Health Organization says the numbers are likely an undercount.
The past two weeks, Israel has allowed around triple the amount of food into Gaza than had been entering since late May. That followed 2 1/2 months when Israel barred all food, medicine and other supplies, saying it was to pressure Hamas to release hostages taken during its 2023 attack that launched the war. The new influx has brought more food within reach for some of the population and lowered some prices in marketplaces, though it remains far more expensive than prewar levels and unaffordable for many.
While better food access might help much of Gaza’s population, “it won’t help the children who are severely malnourished,” said Alex DeWaal, executive director of the World Peace Foundation at Tufts University, who has worked on famine and humanitarian issues for more than 40 years.
When a person is severely malnourished, vital micronutrients are depleted and bodily functions deteriorate. Simply feeding the person can cause harm, known as “refeeding syndrome,” potentially leading to seizures, coma or death. Instead, micronutrients must first be replenished with supplements and therapeutic milk in a hospital.




